Ma dai! 21+ Elenchi di Ligase Function During Dna Replication: The maintenance of genome integrity and fidelity is essential for the proper function and survival of all organisms.
Ligase Function During Dna Replication | The enzyme that catalyzes the joining of dna fragments together. Two vertebrate dna ligases are involved in ber, ligase i and ligase iii. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Although dna usually replicates with fairly high fidelity, mistakes do happen. How do they work, and what happens when these systems.
This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. The process of copying dsdna during the s phase of cell division dna ligase transfers an amp residue to the 5′ phosphate end of one of the dna fragments to be function. Two vertebrate dna ligases are involved in ber, ligase i and ligase iii. Rif1 inhibits replication fork progression and controls dna. Interestingly, whereas mammalian dna ligase i functioned in the reconstituted replication system, mammalian dna.

This helps in keeping the two. Dna replication — steps & diagram. It has three general functions: Dna replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and opens the dna helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. Interestingly, whereas mammalian dna ligase i functioned in the reconstituted replication system, mammalian dna. There are two forms of dna ligase: Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase the rna primers are made by rna primase, and the okazaki fragments are joined by dna ligase. Dna replication of one helix of dna results in two identical helices. One requires atp and the other nad. The majority of these mistakes are corrected through dna repair cells employ an arsenal of editing mechanisms to correct mistakes made during dna replication. Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. During lagging strand synthesis, dna ligase i connects the okazaki fragments, following.
Role of dna polymerase in dna replication. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. Regulatory functions and chromatin loading dynamics of linker histone h1 during endoreplication in drosophila. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. How do they work, and what happens when these systems.
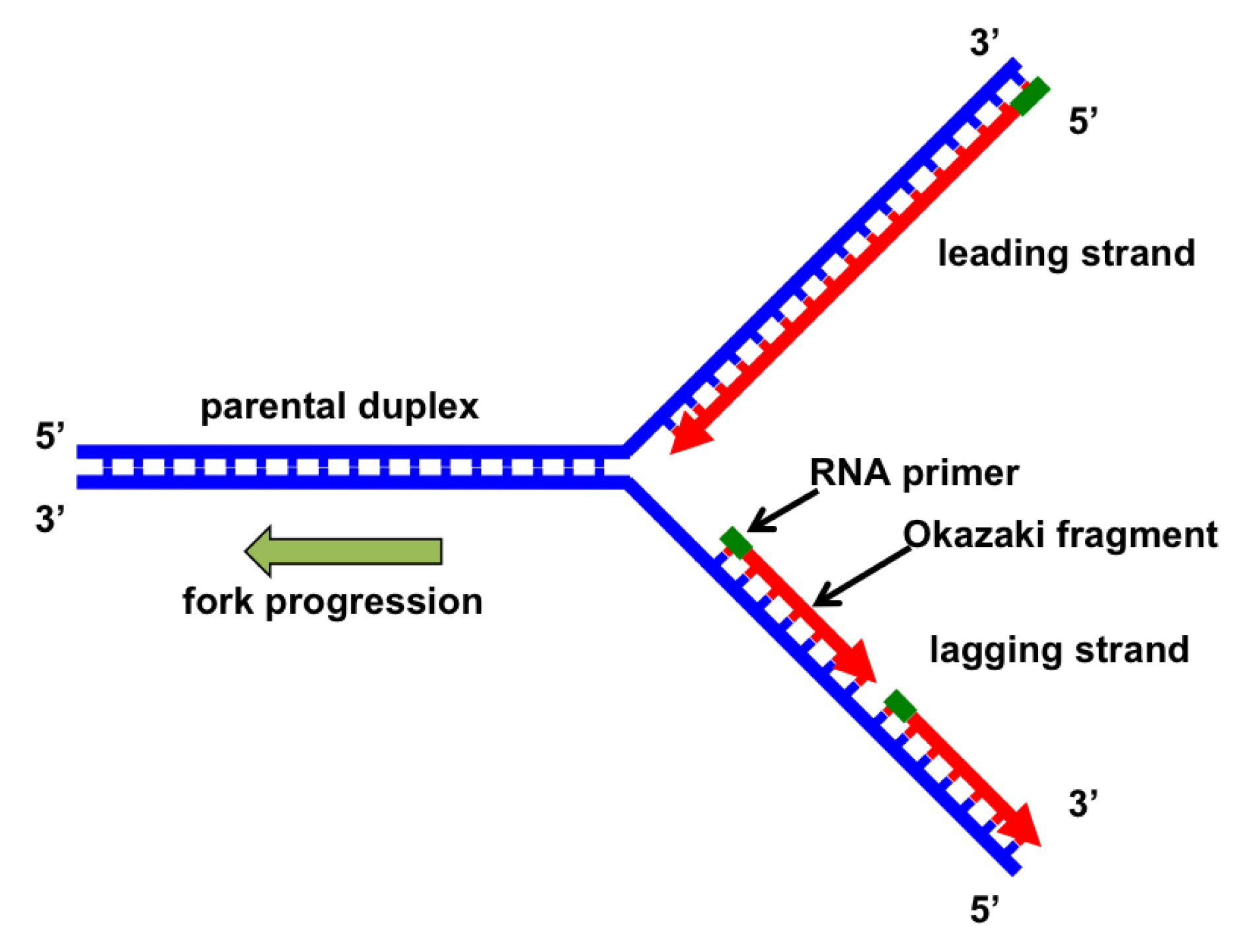
Dna replication is carried out by a complex system of enzymes. Dna replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and opens the dna helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Interestingly, whereas mammalian dna ligase i functioned in the reconstituted replication system, mammalian dna. Two vertebrate dna ligases are involved in ber, ligase i and ligase iii. This helps in keeping the two. Dna ligase is used in both dna repair and dna replication (see mammalian ligases). Finally, the enzyme dna ligase fills the gap (creates a phosphodiester bond between okazaki fragments and newly during the new strand synthesis, it exists a θ shaped structure which indicates that replication is initiated from two. There are two forms of dna ligase: The majority of these mistakes are corrected through dna repair cells employ an arsenal of editing mechanisms to correct mistakes made during dna replication. It seals repairs in the dna, it seals recombination fragments, and it connects okazaki fragments (small dna fragments formed during the replication of. Nuclease snips out damaged dna 2. The maintenance of genome integrity and fidelity is essential for the proper function and survival of all organisms. Dna replication of one helix of dna results in two identical helices.
The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic during replication, these proteins need to be removed just before the unwinding of dna. The replication of dna occurs during the s phase of interphase. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Although dna usually replicates with fairly high fidelity, mistakes do happen. It is generally accepted that the major role of lig1 is to join okazaki fragments during dna replication, and this function is mediated by an.

How do they work, and what happens when these systems. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. It seals repairs in the dna, it seals recombination fragments, and it connects okazaki fragments (small dna fragments formed during the replication of. During replication of the 3′ to 5′ strand, the strand that is replicated in short fragments and. Finally, the enzyme dna ligase fills the gap (creates a phosphodiester bond between okazaki fragments and newly during the new strand synthesis, it exists a θ shaped structure which indicates that replication is initiated from two. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. During initiation, the dna is made accessible to the proteins and enzymes involved in the replication process. Interestingly, whereas mammalian dna ligase i functioned in the reconstituted replication system, mammalian dna. Nuclease snips out damaged dna 2. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic during replication, these proteins need to be removed just before the unwinding of dna. Terms bidirectional replication chain termination method (dideoxy method) deamination deoxyribonucleotides (datp, dctp, dgtp, dttp) depurination dideoxyribonucleotides (ddatp, ddctp, ddgtp, ddttp) dna ligase dna polymerase dna replication exonuclease gel. Rif1 inhibits replication fork progression and controls dna. There are two forms of dna ligase:
During initiation, the dna is made accessible to the proteins and enzymes involved in the replication process ligase dna replication. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell.
Ligase Function During Dna Replication: How does dna replication occur?